Panoptic Segmentation
Panoptic segmentation is a computer vision task that combines semantic segmentation and instance segmentation to provide a comprehensive understanding of the scene. The goal of panoptic segmentation is to segment the image into semantically meaningful parts or regions, while also detecting and distinguishing individual instances of objects within those regions. In a given image, every pixel is assigned a semantic label, and pixels belonging to things classes (countable objects with instances, like cars and people) are assigned unique instance IDs.
Papers and Code
Split&Splat: Zero-Shot Panoptic Segmentation via Explicit Instance Modeling and 3D Gaussian Splatting
Feb 01, 20263D Gaussian Splatting (GS) enables fast and high-quality scene reconstruction, but it lacks an object-consistent and semantically aware structure. We propose Split&Splat, a framework for panoptic scene reconstruction using 3DGS. Our approach explicitly models object instances. It first propagates instance masks across views using depth, thus producing view-consistent 2D masks. Each object is then reconstructed independently and merged back into the scene while refining its boundaries. Finally, instance-level semantic descriptors are embedded in the reconstructed objects, supporting various applications, including panoptic segmentation, object retrieval, and 3D editing. Unlike existing methods, Split&Splat tackles the problem by first segmenting the scene and then reconstructing each object individually. This design naturally supports downstream tasks and allows Split&Splat to achieve state-of-the-art performance on the ScanNetv2 segmentation benchmark.
PanopMamba: Vision State Space Modeling for Nuclei Panoptic Segmentation
Jan 23, 2026Nuclei panoptic segmentation supports cancer diagnostics by integrating both semantic and instance segmentation of different cell types to analyze overall tissue structure and individual nuclei in histopathology images. Major challenges include detecting small objects, handling ambiguous boundaries, and addressing class imbalance. To address these issues, we propose PanopMamba, a novel hybrid encoder-decoder architecture that integrates Mamba and Transformer with additional feature-enhanced fusion via state space modeling. We design a multiscale Mamba backbone and a State Space Model (SSM)-based fusion network to enable efficient long-range perception in pyramid features, thereby extending the pure encoder-decoder framework while facilitating information sharing across multiscale features of nuclei. The proposed SSM-based feature-enhanced fusion integrates pyramid feature networks and dynamic feature enhancement across different spatial scales, enhancing the feature representation of densely overlapping nuclei in both semantic and spatial dimensions. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first Mamba-based approach for panoptic segmentation. Additionally, we introduce alternative evaluation metrics, including image-level Panoptic Quality ($i$PQ), boundary-weighted PQ ($w$PQ), and frequency-weighted PQ ($fw$PQ), which are specifically designed to address the unique challenges of nuclei segmentation and thereby mitigate the potential bias inherent in vanilla PQ. Experimental evaluations on two multiclass nuclei segmentation benchmark datasets, MoNuSAC2020 and NuInsSeg, demonstrate the superiority of PanopMamba for nuclei panoptic segmentation over state-of-the-art methods. Consequently, the robustness of PanopMamba is validated across various metrics, while the distinctiveness of PQ variants is also demonstrated. Code is available at https://github.com/mkang315/PanopMamba.
XD-MAP: Cross-Modal Domain Adaptation using Semantic Parametric Mapping
Jan 20, 2026Until open-world foundation models match the performance of specialized approaches, the effectiveness of deep learning models remains heavily dependent on dataset availability. Training data must align not only with the target object categories but also with the sensor characteristics and modalities. To bridge the gap between available datasets and deployment domains, domain adaptation strategies are widely used. In this work, we propose a novel approach to transferring sensor-specific knowledge from an image dataset to LiDAR, an entirely different sensing domain. Our method XD-MAP leverages detections from a neural network on camera images to create a semantic parametric map. The map elements are modeled to produce pseudo labels in the target domain without any manual annotation effort. Unlike previous domain transfer approaches, our method does not require direct overlap between sensors and enables extending the angular perception range from a front-view camera to a full 360 view. On our large-scale road feature dataset, XD-MAP outperforms single shot baseline approaches by +19.5 mIoU for 2D semantic segmentation, +19.5 PQth for 2D panoptic segmentation, and +32.3 mIoU in 3D semantic segmentation. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach achieving strong performance on LiDAR data without any manual labeling.
ObjectVisA-120: Object-based Visual Attention Prediction in Interactive Street-crossing Environments
Jan 19, 2026The object-based nature of human visual attention is well-known in cognitive science, but has only played a minor role in computational visual attention models so far. This is mainly due to a lack of suitable datasets and evaluation metrics for object-based attention. To address these limitations, we present \dataset~ -- a novel 120-participant dataset of spatial street-crossing navigation in virtual reality specifically geared to object-based attention evaluations. The uniqueness of the presented dataset lies in the ethical and safety affiliated challenges that make collecting comparable data in real-world environments highly difficult. \dataset~ not only features accurate gaze data and a complete state-space representation of objects in the virtual environment, but it also offers variable scenario complexities and rich annotations, including panoptic segmentation, depth information, and vehicle keypoints. We further propose object-based similarity (oSIM) as a novel metric to evaluate the performance of object-based visual attention models, a previously unexplored performance characteristic. Our evaluations show that explicitly optimising for object-based attention not only improves oSIM performance but also leads to an improved model performance on common metrics. In addition, we present SUMGraph, a Mamba U-Net-based model, which explicitly encodes critical scene objects (vehicles) in a graph representation, leading to further performance improvements over several state-of-the-art visual attention prediction methods. The dataset, code and models will be publicly released.
Motion-Compensated Latent Semantic Canvases for Visual Situational Awareness on Edge
Dec 29, 2025We propose Motion-Compensated Latent Semantic Canvases (MCLSC) for visual situational awareness on resource-constrained edge devices. The core idea is to maintain persistent semantic metadata in two latent canvases - a slowly accumulating static layer and a rapidly updating dynamic layer - defined in a baseline coordinate frame stabilized from the video stream. Expensive panoptic segmentation (Mask2Former) runs asynchronously and is motion-gated: inference is triggered only when motion indicates new information, while stabilization/motion compensation preserves a consistent coordinate system for latent semantic memory. On prerecorded 480p clips, our prototype reduces segmentation calls by >30x and lowers mean end-to-end processing time by >20x compared to naive per-frame segmentation, while maintaining coherent static/dynamic semantic overlays.
ICP-4D: Bridging Iterative Closest Point and LiDAR Panoptic Segmentation
Dec 22, 2025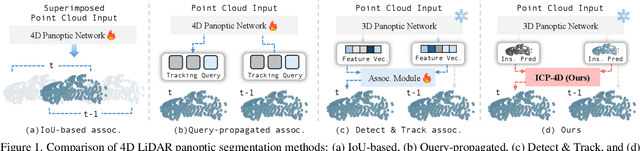
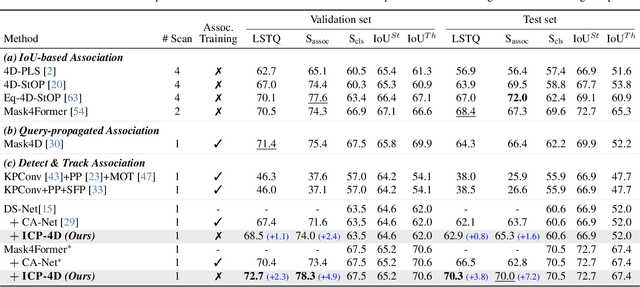
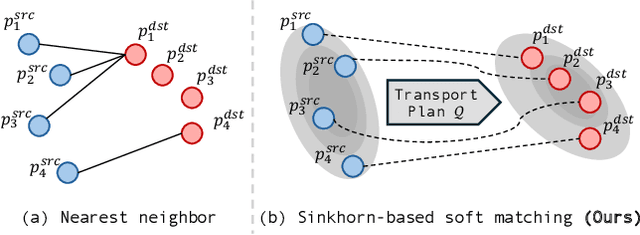
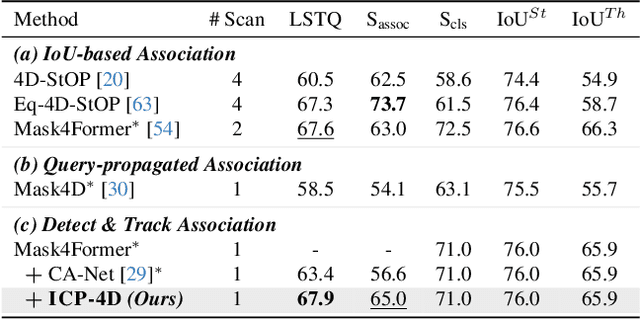
Dominant paradigms for 4D LiDAR panoptic segmentation are usually required to train deep neural networks with large superimposed point clouds or design dedicated modules for instance association. However, these approaches perform redundant point processing and consequently become computationally expensive, yet still overlook the rich geometric priors inherently provided by raw point clouds. To this end, we introduce ICP-4D, a simple yet effective training-free framework that unifies spatial and temporal reasoning through geometric relations among instance-level point sets. Specifically, we apply the Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm to directly associate temporally consistent instances by aligning the source and target point sets through the estimated transformation. To stabilize association under noisy instance predictions, we introduce a Sinkhorn-based soft matching. This exploits the underlying instance distribution to obtain accurate point-wise correspondences, resulting in robust geometric alignment. Furthermore, our carefully designed pipeline, which considers three instance types-static, dynamic, and missing-offers computational efficiency and occlusion-aware matching. Our extensive experiments across both SemanticKITTI and panoptic nuScenes demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, even without additional training or extra point cloud inputs.
With Great Context Comes Great Prediction Power: Classifying Objects via Geo-Semantic Scene Graphs
Dec 28, 2025Humans effortlessly identify objects by leveraging a rich understanding of the surrounding scene, including spatial relationships, material properties, and the co-occurrence of other objects. In contrast, most computational object recognition systems operate on isolated image regions, devoid of meaning in isolation, thus ignoring this vital contextual information. This paper argues for the critical role of context and introduces a novel framework for contextual object classification. We first construct a Geo-Semantic Contextual Graph (GSCG) from a single monocular image. This rich, structured representation is built by integrating a metric depth estimator with a unified panoptic and material segmentation model. The GSCG encodes objects as nodes with detailed geometric, chromatic, and material attributes, and their spatial relationships as edges. This explicit graph structure makes the model's reasoning process inherently interpretable. We then propose a specialized graph-based classifier that aggregates features from a target object, its immediate neighbors, and the global scene context to predict its class. Through extensive ablation studies, we demonstrate that our context-aware model achieves a classification accuracy of 73.4%, dramatically outperforming context-agnostic versions (as low as 38.4%). Furthermore, our GSCG-based approach significantly surpasses strong baselines, including fine-tuned ResNet models (max 53.5%) and a state-of-the-art multimodal Large Language Model (LLM), Llama 4 Scout, which, even when given the full image alongside a detailed description of objects, maxes out at 42.3%. These results on COCO 2017 train/val splits highlight the superiority of explicitly structured and interpretable context for object recognition tasks.
Consistent Instance Field for Dynamic Scene Understanding
Dec 16, 2025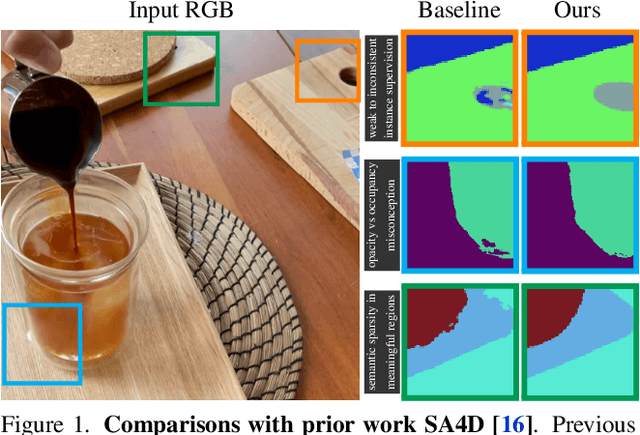
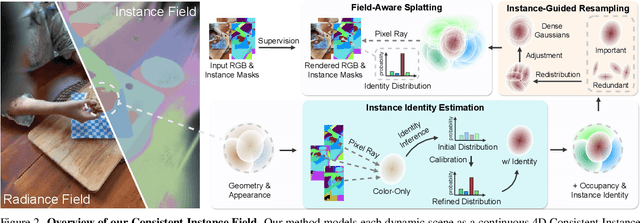
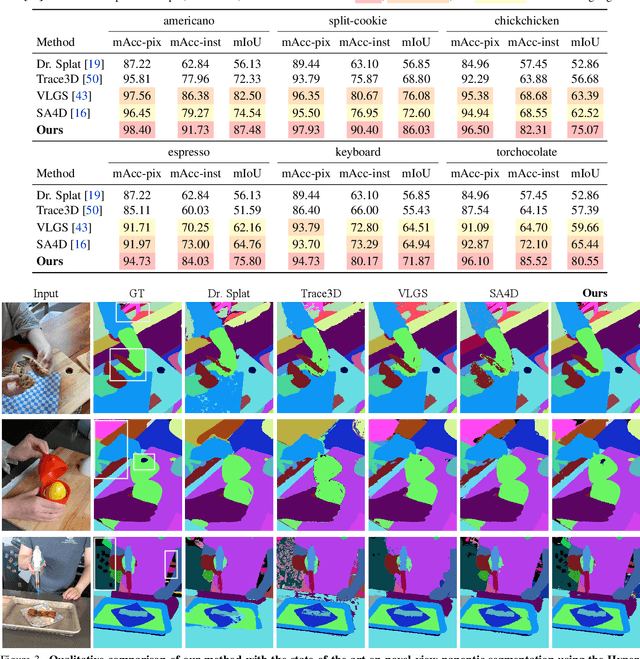
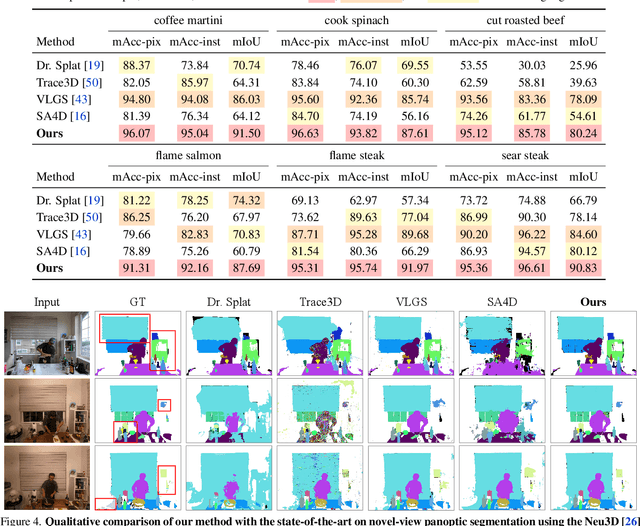
We introduce Consistent Instance Field, a continuous and probabilistic spatio-temporal representation for dynamic scene understanding. Unlike prior methods that rely on discrete tracking or view-dependent features, our approach disentangles visibility from persistent object identity by modeling each space-time point with an occupancy probability and a conditional instance distribution. To realize this, we introduce a novel instance-embedded representation based on deformable 3D Gaussians, which jointly encode radiance and semantic information and are learned directly from input RGB images and instance masks through differentiable rasterization. Furthermore, we introduce new mechanisms to calibrate per-Gaussian identities and resample Gaussians toward semantically active regions, ensuring consistent instance representations across space and time. Experiments on HyperNeRF and Neu3D datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on novel-view panoptic segmentation and open-vocabulary 4D querying tasks.
Orion: A Unified Visual Agent for Multimodal Perception, Advanced Visual Reasoning and Execution
Nov 18, 2025We introduce Orion, a visual agent framework that can take in any modality and generate any modality. Using an agentic framework with multiple tool-calling capabilities, Orion is designed for visual AI tasks and achieves state-of-the-art results. Unlike traditional vision-language models that produce descriptive outputs, Orion orchestrates a suite of specialized computer vision tools, including object detection, keypoint localization, panoptic segmentation, Optical Character Recognition, and geometric analysis, to execute complex multi-step visual workflows. The system achieves competitive performance on MMMU, MMBench, DocVQA, and MMLongBench while extending monolithic vision-language models to production-grade visual intelligence. By combining neural perception with symbolic execution, Orion enables autonomous visual reasoning, marking a transition from passive visual understanding to active, tool-driven visual intelligence.
Canonical Space Representation for 4D Panoptic Segmentation of Articulated Objects
Nov 07, 2025Articulated object perception presents significant challenges in computer vision, particularly because most existing methods ignore temporal dynamics despite the inherently dynamic nature of such objects. The use of 4D temporal data has not been thoroughly explored in articulated object perception and remains unexamined for panoptic segmentation. The lack of a benchmark dataset further hurt this field. To this end, we introduce Artic4D as a new dataset derived from PartNet Mobility and augmented with synthetic sensor data, featuring 4D panoptic annotations and articulation parameters. Building on this dataset, we propose CanonSeg4D, a novel 4D panoptic segmentation framework. This approach explicitly estimates per-frame offsets mapping observed object parts to a learned canonical space, thereby enhancing part-level segmentation. The framework employs this canonical representation to achieve consistent alignment of object parts across sequential frames. Comprehensive experiments on Artic4D demonstrate that the proposed CanonSeg4D outperforms state of the art approaches in panoptic segmentation accuracy in more complex scenarios. These findings highlight the effectiveness of temporal modeling and canonical alignment in dynamic object understanding, and pave the way for future advances in 4D articulated object perception.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge